New ACORE Report Assesses Growing Confidence for Renewable Energy Finance in the Aftermath of the Pandemic
By: Maheen Ahmad and Lesley Hunter
June 17, 2021
ACORE’s recently released report, Expectations for Renewable Energy Finance in 2021-2024, finds that confidence in the renewable energy and energy storage sectors is at an all-time high. With the economy starting to emerge from the COVID pandemic, the report assesses progress on ACORE’s $1T 2030 campaign and presents the results of two new surveys of professionals who represent companies that actively finance or develop projects in the renewable energy sector. The surveys assess respondents’ experiences in the market over the past year and their expectations for sector investment and development over the next three years.
ACORE launched its $1T 2030 campaign in 2018 to achieve $1 trillion in private sector investment in U.S. renewable energy and enabling grid technologies by 2030, while advocating for policy reforms and market drivers to help meet this goal. One trillion dollars of investment over these 12 years would represent more than two times the historic investment in the U.S. renewable sector before the campaign and help get us on a trajectory toward achievement of President Biden’s goal for a carbon-free grid by 2035. Following are some key highlights from this year’s report.
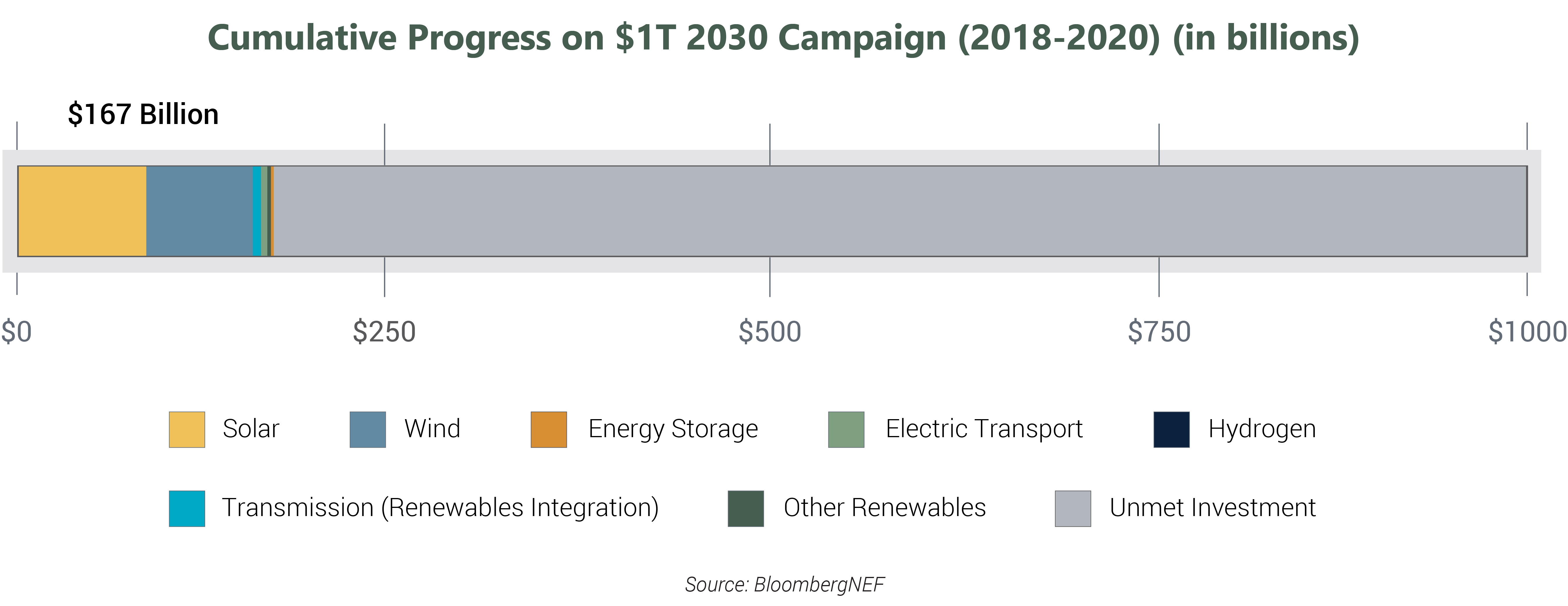
The U.S. has reached 17% of the $1T 2030 campaign goal.
The U.S. has now attracted $167 billion in investment for renewable energy, grid-enabling technologies and transmission for renewable integration since the $1T 2030 campaign launch in 2018. Achieving the 2030 objective will require an average of $92.6 billion in annual investment through 2029, an annual increase of 59 percent over the 2020 investment level.
Asset finance investment in the U.S. renewable energy and grid-enabling technology sectors decreased in 2020 to $58.3 billion, even as the solar and energy storage sectors had record years.
Renewable sector investment decreased 12 percent in 2020, primarily due to lower financings in the onshore wind sector. A central reason for the decrease is that credits for new wind energy development were scheduled to phase out at the end of 2020. While Congress extended the wind production tax credit in December, investors had little opportunity to take advantage of this change. Wind investment, therefore, peaked in 2019 as developers rushed to take advantage of the about-to-expire tax credits. Meanwhile, solar investment increased 36% from 2019, and investment in energy storage passed $1 billion in annual investment for the first time.
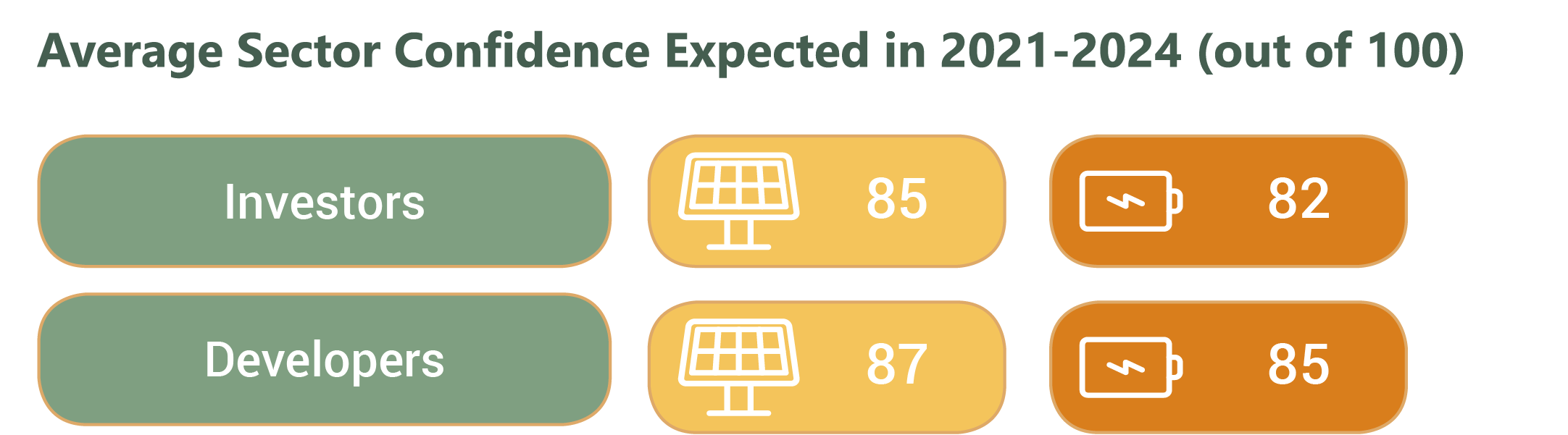
Surveyed investors and developers report, on average, even higher confidence levels in the renewable energy and energy storage sectors than in ACORE’s past surveys, which have always reflected strong optimism.
For the renewable energy sector, investor confidence increased by an average of eight points and developer confidence increased by nine points. More than two-thirds of surveyed investors (68%) report plans to increase their investments by more than 10 percent this year compared to 2020. Similarly, developers plan to maintain or increase their activity in 2021 compared to 2020. Eighty-seven percent of developers indicate that the December 2020 federal tax credit and safe harbor extensions affected their decision-making in 2021.
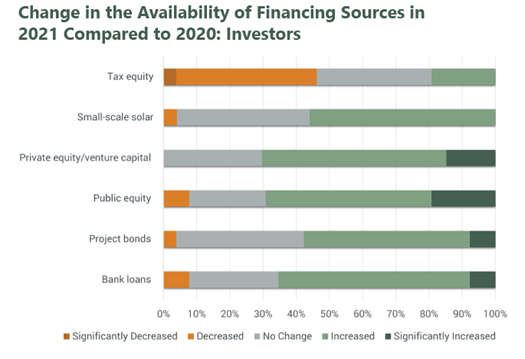
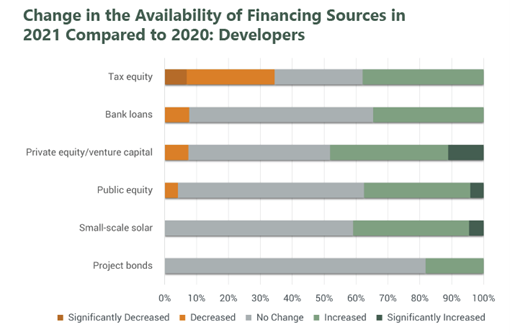
Risk appetites have increased, but survey respondents report challenges securing tax equity financing and for hedge agreements.
Nearly all surveyed investors (90%) and developers (93%) report either maintained or increased risk appetites in 2021 compared to 2020. However, some respondents cite reduced access to specific financing sources and consequences from the February 2021 Texas power outages as impediments to business.
Investors and developers continue to report shortages in tax equity in 2021, as also observed in ACORE’s 2020 surveys. A higher proportion of both investors and developers report a decrease in tax equity than any other financing source. Interest in hedged merchant renewable or storage agreements has remained unchanged or increased for most survey respondents in 2021; however, 23 percent of investors and 30 percent of developers report a decrease or significant decrease in interest in hedge agreements, citing repercussions from the Texas power outages.
Energy storage and utility-scale solar rank as the most popular preferences for investment among surveyed investors over the next three years.
This is the fourth consecutive year that energy storage either led or tied as most attractive asset class for investment. Also notable is the elevation of offshore wind, which for the first time comes in ahead of onshore wind in fourth place, as well as the impressive first-time appearance of green hydrogen at number seven.

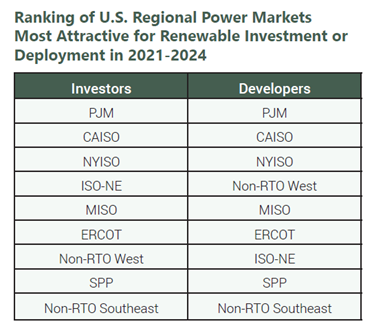
PJM, CAISO and NYISO rank as the most attractive U.S. regions for renewable energy investment and development over the next three years.
While PJM, CAISO and NYISO receive top rankings from both investors and developers, survey results indicate that ERCOT’s appearance as sixth on the list may be attributable to the market uncertainty caused by the February outages and proposed anti-renewable legislation in the Lone Star state.
Looking forward, most investors and developers select long-term extensions of the wind and solar tax credits and a new standalone energy storage tax credit as effective federal policy options for growing the sector.
Both investors and developers also emphasize the importance of market reforms and financial incentives to facilitate the expansion of high-voltage transmission lines, which can enable more renewable energy deployment.
ACORE is strategically deploying its resources to promote key policy reforms and market drivers to support the achievement of the $1 trillion by 2030 objective.
Specifically, we are pursuing the following priorities in 2021:
-
- Tax Policy: ACORE works to protect and extend existing incentives for renewable energy and provide a long-term level playing field in support of carbon-free electricity generation, including a free-standing investment tax credit for energy storage technologies and regionally significant transmission.
- Climate Policy: ACORE focuses on identifying and promoting the most viable suite of climate policies and analyzes their impact on renewable energy growth and investment, including a federal high-penetration renewable energy standard or clean energy standard and carbon pricing.
- Grid Advocacy: ACORE advocates for cost-effective investment in transmission infrastructure to create a Macro Grid, and a less balkanized and fairer electricity marketplace to promote greater access to and delivery of renewable resources.
- Energy Storage: Energy storage and other grid-enabling technologies have the potential to transform the power system and fundamentally change the way we think about energy. ACORE promotes their growth through policy advocacy, market reforms and financing solutions.
- Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Scoring: ACORE works with its members to increase standardization, transparency and use of material indicators in ESG disclosure and scoring methodologies through specific recommendations and regular outreach to the ESG community.
Read the full report here: https://acore.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Expectations-for-Renewable-Energy-Finance-in-2021-2024-ACORE.pdf
Join leaders from across the renewable energy sector.

What will our next 20 years look like? Here’s the truth: they’ll be better with ACORE at the forefront of energy policy.
Shannon Kellogg
Amazon Web Services (AWS)