- Energy Storage & Decarbonization Pathways
- Project Finance
- Sustainable Investing & ESG
- Tax Incentives & Appropriations
- Blog
New ACORE Analysis Reflects on U.S. Renewable Energy and Energy Storage Finance Amid COVID-19
By: Lesley Hunter and Maheen Ahmad
July 14, 2020
As the renewable sector faces the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, ACORE’s new analysis, Expectations for Renewable Energy Finance in 2020-2023, collates industry perspectives on the near-term environment for renewable finance and assesses progress on ACORE’s $1T 2030 campaign. ACORE launched the $1T 2030 campaign in 2018 to achieve $1 trillion in private sector investment in U.S. renewable energy and enabling grid technologies by 2030, while advocating for the policy and market reforms to help realize this goal. To assess the impact of COVID-19 on investment and business strategies, ACORE surveyed several prominent financial institutions and renewable developers to gauge their near- and mid-term confidence in the sector.
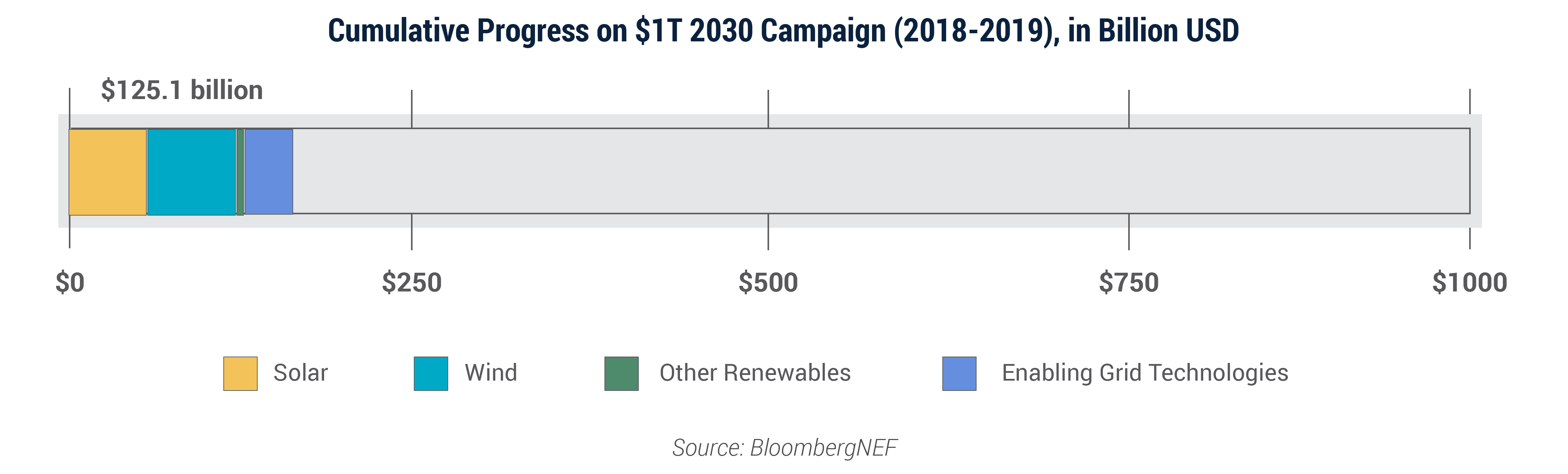
The United States reached almost 13% of the campaign goal in 2019.
The U.S. has now attracted $125.1 billion in private sector investment in renewable energy and enabling grid technologies since the launch of the $1T 2030 campaign in 2018.
Achieving the 2030 goal will now require an average of $87.5 billion per year in private sector investment through 2029 – an annual increase of 28% over the 2019 investment level.
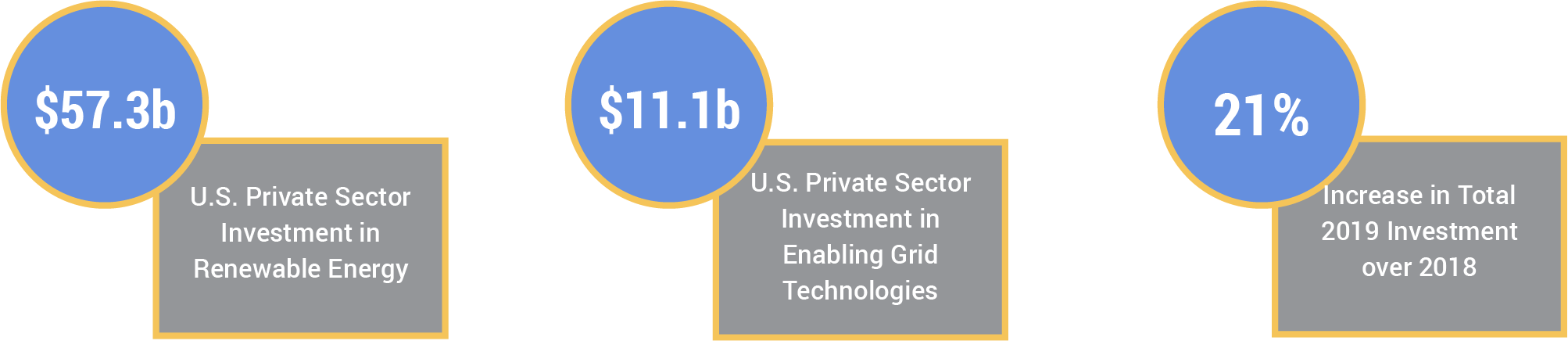
Private sector investment in U.S. renewable energy and enabling grid technology reached its highest level to date at $68.4 billion in 2019.
This record year marked a 21% increase over the 2018 investment level. The growth was largely driven by phasedown schedules for the federal tax credits, expanded state renewable energy standards, growing cost competitiveness, and increased demand from corporate buyers, residential consumers, electric utilities and investors focused on sustainability.
The pandemic has presented new challenges for renewable energy and energy storage investment.
COVID-19 has led to the loss of almost 100,000 jobs in the renewable energy sector, strained renewable energy project financing and caused innumerable project delays. These impacts are expected to reduce the amount of new renewable energy capacity in 2020 by 21%.

However, renewable energy investors and developers remain confident in the longer-term growth of the sector.
ACORE surveyed prominent utility-scale renewable energy companies to determine the extent of COVID-19’s impact on renewable energy investment and finance. While companies are experiencing significant headwinds in 2020, surveyed renewable energy investors remain as confident in renewable energy growth over the next three years, on average, as they were in 2018-2019. They are similarly confident in their expectations of rapid energy storage growth. In both sectors, the strong investor confidence is mirrored by high confidence levels from renewable energy developers.
Over half of surveyed financial institutions plan to increase their investment in renewables by more than 10% in 2020 compared to 2019. Energy storage and utility-scale solar rank as the most popular preferences for investment among surveyed investors over the next three years. Over the same time frame, investors consider the U.S. to be an attractive venue for investment compared to leading countries like China.
In the near term, survey respondents are most concerned about COVID-19’s impact on the ability to attract project finance, particularly tax equity investment.
Most surveyed investors and developers do not expect the COVID-19 pandemic to have a long-term impact on their business plans, but many are experiencing short-term difficulties with financing and project delays. Two-thirds of surveyed developers report difficulty in securing financing or offtakers for projects, and some cite project delays of up to 12 months. Three-quarters of surveyed investors predict a decline in tax equity financing, an important source of capital for project finance, which could have both short- and longer-term impacts on renewable energy development.
To support achievement of the $1 trillion by 2030 objective, ACORE is strategically deploying its resources to promote key policy reforms and market drivers in 2020.
-
-
-
- COVID-19 Response: ACORE advocates for policy solutions to help the sector recover from the COVID-19 pandemic, including measures to facilitate the monetization of renewable energy tax credits and a delay in their phasedown schedules.
-
-
-
-
-
- Climate Policy: ACORE focuses on identifying the most viable suite of climate policies and analyzes their impact on renewable energy growth and investment, including a federal high-penetration renewable or clean energy standard, a technology-neutral tax credit, and carbon pricing.
- Grid Advocacy: ACORE advocates for cost-effective investment in transmission and distribution infrastructure, including a new Macro Grid that better connects population centers with areas richest in regional resources, and a less balkanized and fairer electricity marketplace to promote greater access to, and delivery of, renewable power.
-
-
-
-
-
- Energy Storage: Energy storage and other grid-enabling technologies have the potential to transform the electricity system and fundamentally change the way we think about energy. ACORE promotes their growth through advocacy for a standalone energy storage tax credit and other supportive policies, market reforms and financing solutions.
-
-
-
-
-
- Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Scoring: ACORE works with its members to increase standardization, transparency and use of material indicators in ESG disclosure and scoring processes through specific recommendations and regular outreach to the ESG community.
-
-
Join leaders from across the clean energy sector.

What will our next 20 years look like? Here’s the truth: they’ll be better with ACORE at the forefront of energy policy.
Shannon Kellogg
Amazon Web Services (AWS)